Difference between machine tap and hand tap
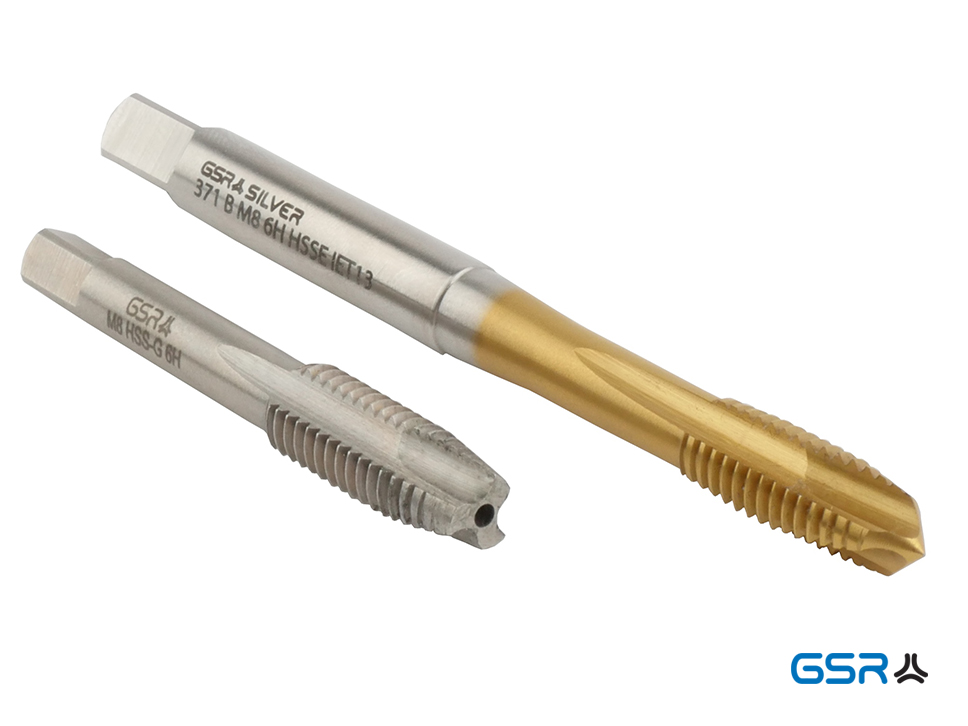

Machine tap vs hand tap
The main difference between hand taps and machine taps lies in their design and intended use. Here’s a breakdown of the distinctions:
Hand Taps:
Design: Hand taps, also known as plug taps, are designed for manual operation with a tap handle or tap wrench. They typically have a square or hexagonal shank at one end for gripping with a tool.
Chamfer Style:
Hand taps often have a tapered chamfer at the front end (starting thread) to facilitate easy entry into the workpiece. This taper gradually transitions into a full thread profile.
Flute Design:
Hand taps usually have straight flutes that extend the entire length of the tap. The straight flutes help with chip evacuation when hand tapping.
Versatility:
Hand taps are versatile and can be used for both through-hole and blind-hole applications. They are suitable for smaller projects or situations where only a few threads need to be created.
Control and Feel:
Hand tapping offers more control and tactile feedback compared to machine tapping. The operator can adjust the speed, feed rate, and pressure applied during the tapping process based on the feel and feedback from the tool.
Machine Taps:
Design:
Machine taps, also known as spiral flute taps or spiral point taps, are specifically designed for use with tapping machines, drill presses, or tapping attachments. They often have a cylindrical shank for secure attachment to the machine.
Chamfer Style:
Machine taps typically have a plug chamfer or a bottoming chamfer. The plug chamfer is suited for general-purpose tapping, while the bottoming chamfer is used when threading to the bottom of a blind hole.
Flute Design:
Machine taps can have either spiral flutes or straight flutes. Spiral flute taps have curved flutes that twist around the tap body, aiding in chip evacuation. Straight flute taps are less common for machine tapping.
High-Speed Operation:
Machine taps are designed for higher rotational speeds and are well-suited for production environments where speed and efficiency are crucial. They are used with tapping machines or attachments that provide controlled speed and feed rates.
Chip Evacuation:
The spiral design of machine taps, especially spiral flute taps, facilitates efficient chip evacuation during the tapping process. This helps prevent chip buildup and improves cutting performance.
Accuracy and Consistency:
Machine tapping offers greater precision, repeatability, and uniform thread quality compared to hand tapping. The use of tapping machines or attachments ensures consistent speed, feed, and depth control.
It’s important to note that while hand taps and machine taps have distinct characteristics, there can be some overlap in their usage. Hand taps can also be used with tapping machines or power tools, although machine taps are generally more optimized for high-speed, production-oriented tapping processes.
When choosing between hand taps and machine taps, consider factors such as the application, desired thread quality, production volume, and available equipment.
People also ask
Excavator digger bucket
An excavator digger bucket is a specific type of bucket attachment designed for digging and excavating tasks. It is one of the most commonly used attachments for excavators. The digger bucket typically features a curved shape with teeth or cutting edges along the front edge to penetrate and scoop through soil, sand, gravel, or other loose materials. The size and capacity of the digger bucket can vary depending on the excavator’s size and the intended application. These buckets are essential for earthmoving, trenching, and general excavation work, allowing the excavator to efficiently remove and transport materials from the digging site.